Mastering Coronary Angiography: Image Intensifier & C-arm Fundamentals
Medmastery・4 minutes read
X-rays emitted from an x-ray source create a geographic image detected by an image intensifier in the cath lab, while the SI arm allows for capturing various anatomical views by moving around the patient and rotating at specific angles denoting positions like RAO 30 or LAO 40.
Insights
- The process of acquiring a geographic image involves emitting x-rays from a source, detecting them with an image intensifier connected by an SI arm in the cath lab, and positioning the patient in the x-ray beam to capture different anatomical views.
- Various views, like right anterior oblique (RAO) or left anterior oblique (LAO), are obtained by rotating the image intensifier around the patient at specific angles, such as RAO 30 or LAO 40, showcasing the intricate and precise nature of cardiac imaging techniques.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
How are x-ray images obtained in a cath lab?
X-ray images in a cath lab are acquired by emitting x-rays from a source and detecting them with an image intensifier connected by an SI arm. The patient is positioned in the x-ray beam, focusing on the heart, and the SI arm moves around the patient to capture various anatomical views. Different views, like RAO or LAO, are obtained by rotating the image intensifier around the patient at specific angles.
What is the purpose of the SI arm in a cath lab?
The SI arm in a cath lab serves the purpose of moving around the patient to capture different anatomical views. It allows for the rotation of the image intensifier to obtain specific views like RAO or LAO by positioning it at precise angles denoted by numbers, such as RAO 30 or LAO 40.
How does the x-ray source function in a cath lab?
In a cath lab, the x-ray source emits x-rays that are used to acquire geographic images of the patient's anatomy. These x-rays are detected by an image intensifier connected by an SI arm, which moves around the patient to capture various views by rotating the intensifier at specific angles.
What are the different anatomical views obtained in a cath lab?
In a cath lab, various anatomical views are obtained by rotating the image intensifier around the patient. Views like right anterior oblique (RAO) or left anterior oblique (LAO) are captured by positioning the intensifier at specific angles, such as RAO 30 or LAO 40, to visualize different aspects of the heart and surrounding structures.
How is the patient positioned for x-ray imaging in a cath lab?
In a cath lab, the patient is positioned in the x-ray beam to focus on the heart, allowing for the acquisition of geographic images. The SI arm connected to the image intensifier moves around the patient in different directions to capture various anatomical views by rotating the intensifier at specific angles like RAO 30 or LAO 40.
Related videos

White Board and Marker Cardiology Lectures
Basics of angiographic views during left heart catheterization
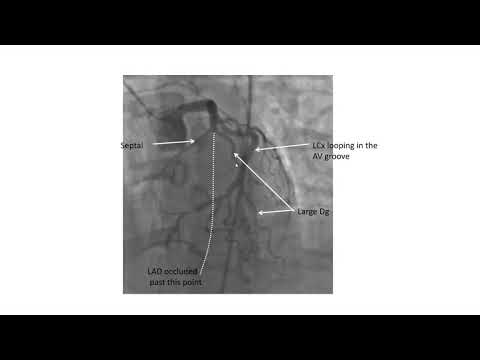
Elias Hanna
Coronary angiographic views- Elias Hanna

Med School Insiders
So You Want to Be a RADIOLOGIST [Ep. 16]

Sononerds
Basic Abdominal Ultrasound Imaging :: Unit 1 :: Normal Abdomen Ultrasound with Sononerds

POCUS 101
Basic Transthoracic Echocardiography (Cardiac Ultrasound) - TTE Made Simple
Summary
00:00
"X-ray source captures heart anatomy views"
- To acquire a geographic image, an x-ray source emits x-rays and is detected by an image intensifier connected by an SI arm in the cath lab.
- The patient is positioned in the x-ray beam centering on the heart, with the SI arm able to move around the patient in different directions to capture various anatomical views.
- Different views are obtained by rotating the image intensifier around the patient, such as right anterior oblique (RAO) or left anterior oblique (LAO), with specific angles denoting the position, like RAO 30 or LAO 40.




