K-Bio Matter 7: Cells 1- Cell Size
David Knuffke・9 minutes read
Cells have size limits with the upper limit constrained by material transport efficiency, leading to decreased efficiency as size increases. Cells adapt to maximize surface area to volume ratio for better functionality and absorption capabilities.
Insights
- The size of cells is constrained by both lower and upper limits, with microplasmas representing the smallest observed cells due to essential components, while larger cells face inefficiencies in material transport due to decreased surface area to volume ratio.
- Cells optimize their surface area to enhance material transport efficiency, seen in adaptations like root hairs in plant roots and villi in animal intestines, highlighting the importance of maximizing surface area for cellular functions.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the largest known single-celled organism?
4 inches long
How big are eukaryotic cells compared to prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic: 100 micrometers, Prokaryotic: 10 micrometers
What determines the minimum size of a cell?
Essential components for functions
Why do larger cells become less efficient in material transport?
Surface area to volume ratio decreases
How do cells adapt to maximize surface area for efficient material transport?
Plant roots grow root hairs, animal intestines have villi and microvilli
Related videos

The Science Break
Diffusion II Exchange Surfaces For AQA 9-1 GCSE Biology and Trilogy (Combined Science)
Bozeman Science
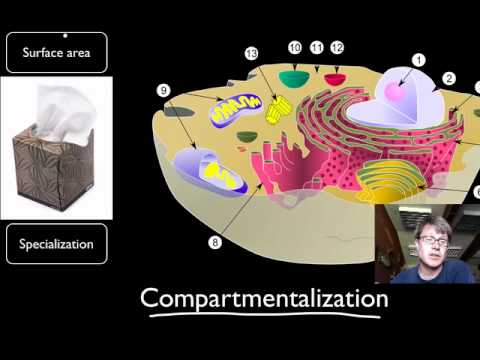
Compartmentalization

FuseSchool - Global Education
Unicellular vs Multicellular | Cells | Biology | FuseSchool

Osmosis from Elsevier
Endocytosis and exocytosis

CrashCourse
In Da Club - Membranes & Transport: Crash Course Biology #5
Summary
00:00
Cell Size Limits and Adaptations for Efficiency
- Cells have size limits, with most being microscopic, and the largest known single-celled organism being about 4 inches long.
- Eukaryotic cells are typically around 100 micrometers in size, while prokaryotic cells are much smaller at about 10 micrometers.
- The minimum size of a cell is determined by the essential components needed for its functions, with microplasmas being among the smallest observed cells.
- The upper limit of cell size is constrained by the efficiency of material transport, as larger cells become less efficient due to the surface area to volume ratio.
- The surface area to volume ratio decreases as cell size increases, leading to inefficiency in material transport and ultimately limiting cell size.
- Cells adapt to maximize surface area, such as plant roots growing root hairs and animal intestines having villi and microvilli to enhance absorption capabilities.




