Jewish Denominations Explained
UsefulCharts・29 minutes read
Matt Baker created a series on Christian denominations and designed a similar tree for Jewish denominations, adapting the concept for Judaism. Judaism emphasizes action over belief for salvation and has evolved over time, developing various sects and regional subcultures, leading to the formation of distinct denominations like Reform, Conservative, and Orthodox branches.
Insights
- Judaism prioritizes following traditions and practices over specific beliefs for salvation, emphasizing the present benefits of mitzvot, akin to obeying traffic laws for safety rather than avoiding punishment.
- Ashkenazi Jews, originating in southern Italy before settling in Germany around 800 AD, form a distinct ethnic group with clear DNA markers tracing back to the Middle East, debunking the theory of Khazar descent, and were predominantly pushed into Eastern Europe until the 20th century.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What are the main branches of modern Judaism?
Three main branches: Reform, Conservative, and Orthodox.
How did Ashkenazi Jews originate?
Originated in southern Italy before settling in Germany.
What are the major sects of Second Temple Judaism?
Pharisees, Essenes, Zealots, and Sadducees.
How did Judaism evolve from ancient Israelite religion?
Influenced by Zoroastrianism and Hellenism, becoming monotheistic.
What are the regional subcultures of Judaism post-1740?
Sephardic, Ashkenazi, and Mizrahi Jews.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
"Matt Baker explores Jewish denominations and history"
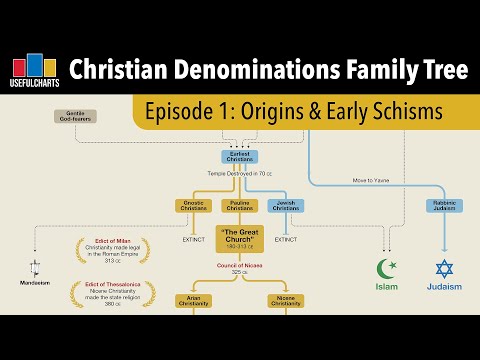
- Matt Baker completed an eight-part series on Christian denominations and was requested to create a similar tree for Jewish denominations.
- The concept of denominations differs between Christianity and Judaism, but Matt aims to adapt it for Jewish denominations.
- Matt acknowledges Dr. Henry Abramson and viewers for feedback and recommends Dr. Abramson's YouTube channel on Jewish history.
- Christianity and Judaism differ in their focus on belief versus action, with Christianity emphasizing belief for salvation.
- Judaism prioritizes following traditions and practices over specific beliefs for salvation, with a focus on the present benefits of mitzvot.
- Judaism's emphasis on action is likened to obeying traffic laws for safety rather than for avoiding punishment.
- Judaism evolved from ancient Israelite religion, influenced by Zoroastrianism and Hellenism, becoming monotheistic by the time of the Romans.
- Second Temple Judaism had four major sects - Pharisees, Essenes, Zealots, and Sadducees, with only the Pharisees surviving.
- Rabbinic Judaism developed after the destruction of Jerusalem, focusing on communal prayer and Torah study led by rabbis.
- Regional subcultures like Sephardic, Ashkenazi, and Mizrahi Jews emerged post-1740, but Judaism remained unified without denominational divisions.
17:35
Ashkenazi Jews: Origins, Diversity, and Branches
- Ashkenazi Jews settled in various regions, including the Ottoman Empire, North Africa, the low countries, and the new world before becoming dominant.
- Recent DNA studies reveal that Ashkenazi Jews originated in southern Italy before settling in Germany around 800 AD.
- A genetic bottleneck occurred when Ashkenazi Jewish numbers dwindled to around 350 people, leading to intermarriage within the group.
- Ashkenazi Jews are a distinct ethnic group with clear DNA markers, tracing back to the Middle East despite partial European ancestry.
- The theory that Ashkenazi Jews descended from the Khazars and are fake Jews is debunked.
- Ashkenazi Jews, originally settled in Germany, were mostly pushed into Eastern Europe until the 20th century.
- Mizrahi Jews, a catch-all term for those who never left the Middle East, assimilated Sephardic customs.
- The division between Sephardic and Ashkenazi Jews is based on customs, not theological differences.
- Modern Judaism has three main branches: Reform, Conservative, and Orthodox, differing in their approach to Jewish law (halacha).
- Reconstructionist and Renewal Judaism are additional branches, with Reconstructionist valuing tradition and distinct Jewish identity, while Renewal incorporates mystical elements from Hasidic Judaism.
35:13
Diverse Jewish Denominations Across Countries
- In the U.S, Sephardic Jews may not align with the three main streams of Judaism, and there are also humanist Jews who celebrate holidays despite not believing in God. Messianic Jews are essentially Christians, discussed in a previous episode on Christian denominations.
- In the UK, there are two major reform denominations that recently announced a merger, along with a chief Rabbi for Orthodox Jews who participated in King Charles III's coronation. In Israel, Jews are categorized into secular (haloni), traditional (mazorti), and observant (dati and haredi) groups, with religious matters overseen by two Chief Rabbis representing Ashkenazi and Sephardi Jews.