Introduction to Geometry
The Organic Chemistry Tutor・21 minutes read
Lines, rays, and segments have distinct characteristics in geometry, angles are classified based on their measurements, and proving triangle congruence relies on various postulates and principles such as SAS, ASA, AAS, SSS, and CPCTC. Triangle congruence can be demonstrated through shared sides and angles using postulates like ASA, while altitude and congruent angles aid in proving angle congruence within a triangle.
Insights
- Lines in geometry extend infinitely in opposite directions, while rays have a starting point and continue indefinitely in one direction.
- Proving triangle congruence relies on postulates like SAS, ASA, AAS, and SSS, with the CPCTC principle ensuring corresponding parts of congruent triangles are also congruent.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the difference between a line and a ray?
A line extends in both directions, while a ray extends in one direction.
Related videos

Khan Academy
Similarity to define sine, cosine, and tangent | Basic trigonometry | Trigonometry | Khan Academy

Shobhit Nirwan - 9th
Triangles Class 9 in One Shot 🔥 | Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 Complete Lecture | Shobhit Nirwan
Justin Backeberg
Geometry 1.1: Identify Points, Lines, and Planes

Problems Beater
icse | class-9th | mathematics | ch-9 |Triangles(congruency in Triangles) | intro | ex-9a | part-1

The Organic Chemistry Tutor
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines, Transversals, Alternate Interior Angles, Alternate Exterior Angles
Summary
00:00
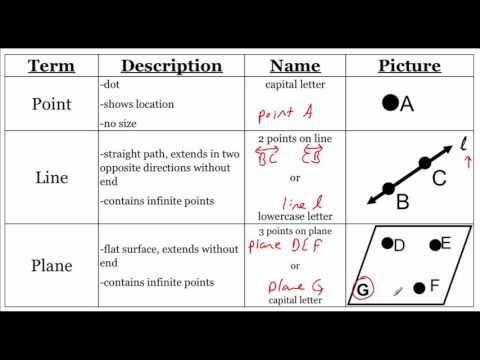
Geometry Basics: Lines, Rays, Segments, and Angles
- A line in geometry extends in opposite directions forever and is denoted with two arrows.
- Points on a line can be named in various ways, such as Line AB, Line BC, or Line AC.
- A ray has a point and extends forever in one direction, starting from the initial point.
- A segment has a beginning and an end, like Segment AB or Segment A.
- Angles include acute (0-90 degrees), right (90 degrees), obtuse (greater than 90 but less than 180 degrees), and straight (180 degrees).
- The midpoint of a segment, like point B in Segment AC, divides it into two equal parts.
- A segment bisector, like Ray RB, divides a segment into two congruent parts.
- An angle bisector, like Ray BD, divides an angle into two equal parts.
- Parallel lines never intersect and have the same slope, denoted by the symbol "||."
- Perpendicular lines intersect at right angles, with slopes being negative reciprocals of each other, symbolized by a right angle symbol.
22:33
Proving Triangle Congruence with Postulates and CPCTC
- To prove triangles congruent, various postulates can be utilized, such as SAS (Side-Angle-Side), ASA (Angle-Side-Angle), AAS (Angle-Angle-Side), and SSS (Side-Side-Side).
- Once triangles are proven congruent, the CPCTC (Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles are Congruent) principle allows for the assertion that corresponding parts of the triangles are also congruent.
- In a scenario where two triangles share a congruent side, splitting them into separate triangles can facilitate proving congruence using the SSS postulate.
- Utilizing the ASA postulate, if two triangles have congruent angles and a shared side, their congruence can be established.
- When given an altitude and congruent angles in a triangle, proving the congruence of specific angles within the triangle can be achieved using the ASA postulate and CPCTC principle.




