Immune System
Amoeba Sisters・7 minutes read
The immune system protects the body from pathogens through external barriers, inflammatory responses, and adaptive immunity involving memory B and T cells, essential for vaccine effectiveness. Memory B and T cells store information to mount faster responses in the future, highlighting the importance of adaptive immunity in protecting against pathogens.
Insights
- The immune system has multiple layers of defense, starting with external barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, followed by an inflammatory response and specific adaptive immunity involving memory B and T cells.
- Memory B and T cells are essential components of adaptive immunity, storing information on pathogens to enable a quicker response in the future and forming the foundation for vaccine efficacy.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the immune system?
The immune system is a network of cells protecting the body from pathogens.
How does the immune system respond to pathogens?
The immune system responds with inflammatory reactions and adaptive immunity.
What are memory B and T cells?
Memory B and T cells store information about pathogens.
How do vaccines work?
Vaccines work by stimulating the immune system's memory cells.
What are the different lines of defense in the immune system?
The immune system has external barriers, inflammatory responses, and adaptive immunity.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
Understanding the Body's Immune System Defense
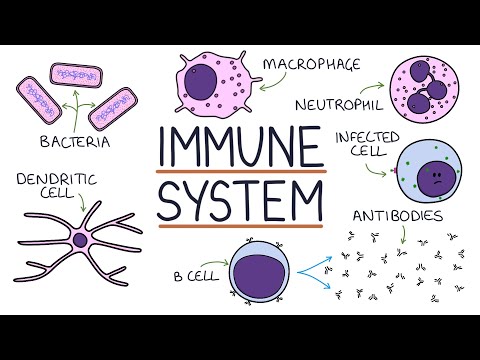
- The immune system is a complex network of cells that work together to protect the body from pathogens like viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites.
- The first line of defense includes external barriers like the skin and mucous membranes that prevent pathogens from entering the body.
- If pathogens breach the first line of defense, the second line of defense involves an inflammatory response, where cells like macrophages consume the pathogens.
- The complement system complements the immune system by attracting macrophages to consume pathogens.
- The third line of defense, adaptive immunity, involves specific responses to antigens, with cell-mediated and humoral responses being key components.
- Memory B and T cells play a crucial role in adaptive immunity, storing information about encountered pathogens to mount a faster response in the future, which is also the basis for vaccine effectiveness.