Humans and the Environment | Essentials of Environmental Science
Hot Mess・15 minutes read
Earth's complex ecosystems are studied in environmental science, which involves various disciplines to address human impacts and environmental issues. Factors like carrying capacity, biodiversity, and threats summarized by HIPPCO highlight the importance of conservation efforts to preserve ecosystems and wildlife populations.
Insights
- Environmental science encompasses various fields like biology, chemistry, economics, politics, and human geography to study Earth's natural systems, human impacts, and solutions to environmental issues.
- Human activities, particularly since the Industrial Revolution, have had a profound impact on Earth's systems, leading to threats like habitat destruction, invasive species, pollution, climate change, and overexploitation that endanger biodiversity, necessitating urgent environmental conservation measures.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is environmental science?
Environmental science studies Earth's natural systems, human impacts, and solutions to environmental issues. It encompasses biology, chemistry, economics, politics, and human geography to understand the interactions between humans and the environment.
How do human activities impact Earth's systems?
Human activities, especially since the Industrial Revolution, have significantly impacted Earth's systems. These activities have led to environmental issues such as habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and overexploitation, affecting ecosystems and biodiversity worldwide.
What are the main threats to biodiversity?
The main threats to biodiversity are summarized by the acronym HIPPCO: Habitat Destruction, Invasive Species, Population Growth, Pollution, Climate Change, and Overexploitation. These factors contribute to the decline of species and ecosystems, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts.
What is the role of biodiversity in ecosystems?
Biodiversity plays a crucial role in the stability and resilience of ecosystems. It encompasses the variety of life forms and interactions within an ecosystem, influencing energy flow, species distribution, and overall ecosystem health.
How do models help in environmental science?
Models are used in environmental science to understand and predict changes in natural systems. These models help researchers and scientists analyze complex environmental issues, make informed decisions, and develop solutions to environmental challenges.
Related videos

UF Thompson Earth Systems Institute TESI
What are Earth Systems?

Khan Academy
Ecology introduction | Ecology | Khan Academy
Magnus Ehinger
Ekosystem

PW English Medium
ORGANISMS & POPULATIONS | Summary in Pure English | Botany | Class 12th Boards

Vidhyaashram
DAY 02 | ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES | II SEM | B.B.A | INTRODUCTION TO ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES | L2
Summary
00:00
"Earth's Environment: Science, Ethics, Solutions"
- Earth is a planet with oceans, forests, clouds, and a variety of life forms that depend on the environment for survival.
- Environmental science studies Earth's natural systems, human impacts, and solutions to environmental issues.
- Environmental science encompasses biology, chemistry, economics, politics, and human geography.
- Environmental ethics include anthropocentrism, biocentrism, and ecocentrism, influencing how questions are asked and answered.
- Human activities, especially since the Industrial Revolution, have significantly impacted Earth's systems.
- Models are used in environmental science to understand and predict changes in natural systems.
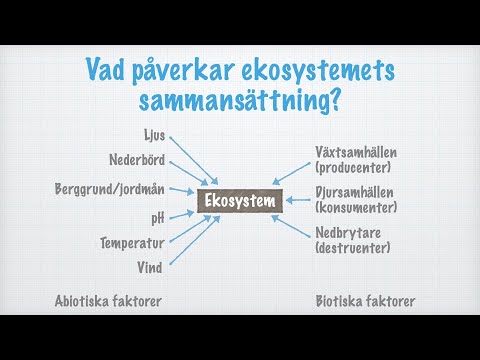
- Biotic and abiotic components interact in ecosystems, with biodiversity playing a crucial role in stability and resilience.
- Food webs and trophic pyramids illustrate energy flow and species distribution in ecosystems.
- Competition and symbiosis are important interactions influencing population growth and dynamics.
- Carrying capacity defines the maximum number of organisms an area can sustain, while endangered species face risks due to various factors like size, specialization, and reproduction rates.
14:39
HIPPCO: Threats to Biodiversity and Conservation
- Main threats to biodiversity are summarized by the acronym HIPPCO: Habitat Destruction, Invasive Species, Population Growth, Pollution, Climate Change, and Overexploitation.
- Habitat loss and fragmentation reduce genetic diversity by separating natural habitats due to human activities like construction, impacting organisms differently based on their home range requirements.
- Invasive species, pollution, climate change, and overexploitation pose significant threats to biodiversity, affecting ecosystems and wildlife populations globally, emphasizing the need for environmental conservation efforts.




