Human Organ Systems – Physiology | Lecturio Nursing
Lecturio Nursing・9 minutes read
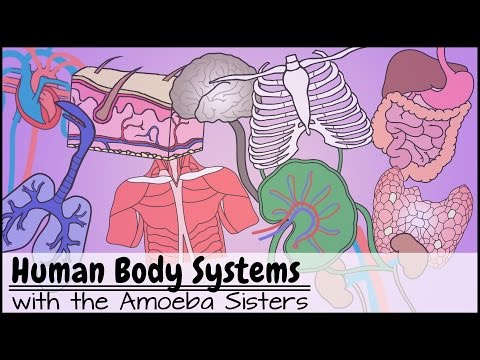
The body has 11 organ systems, each with unique functions and structures. These systems work together to maintain bodily functions and overall health.
Insights
- The integumentary system, encompassing skin, hair, nails, sweat glands, and oil glands, serves multiple crucial functions such as protecting the body, regulating temperature, assisting in waste elimination, and aiding in vitamin D synthesis.
- The cardiovascular system, composed of blood, heart, and blood vessels, plays a pivotal role in circulating oxygenated blood with nutrients to cells, eliminating waste products, and hosting white blood cells for immune defense, showcasing its significance in overall bodily function and health.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the largest organ system in the body?
Integumentary
What does the skeletal system consist of?
Bones, joints, cartilage
What is the main function of the muscular system?
Enable movement and posture maintenance
What is the role of the nervous system in the body?
Detect, interpret, respond to changes
How does the endocrine system regulate body activities?
Releasing hormones
Related videos
Summary
00:00
"Body's 11 Organ Systems: Functions and Roles"
- There are 11 organ systems in the body: muscular, respiratory, skeletal, integumentary, nervous, cardiovascular, lymphatic, urinary, digestive, endocrine, and reproductive.
- The integumentary system is the largest organ system, including the skin, hair, nails, sweat glands, and oil glands. It protects the body, regulates temperature, helps in waste elimination, and aids in vitamin D production.
- The skeletal system comprises bones, joints, and cartilage, supporting and protecting the body, providing muscle attachment surfaces, aiding in movement, and producing red blood cells and storing minerals.
- The muscular system, specifically skeletal muscles, enables movement, posture maintenance, heat production, and body temperature regulation through muscle contractions.
- The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and special sense organs, functioning through action potentials to detect, interpret, and respond to internal and external changes for homeostasis maintenance.
- The endocrine system, including hormone-producing glands and cells, regulates body activities by releasing hormones, working alongside the nervous system but using chemicals for communication.
- The cardiovascular system, comprising blood, heart, and blood vessels, pumps oxygenated blood carrying nutrients to cells, removes waste products, and contains white blood cells for disease defense.