GCE O Level Physics Chapter 3 Dynamics | Physics Revision FULL | Ace With Dennis
Ace With Dennis・14 minutes read
Newton's laws of motion explain the behavior of objects in different scenarios, with the first law emphasizing the need for external forces to change motion and the second law linking force, mass, and acceleration. Various types of forces such as weight, normal force, tension, friction, and air resistance play crucial roles in determining the movement and interactions of objects.
Insights
- Newton's first law explains that objects either stay still or move at a constant speed unless an external force acts on them, as demonstrated by a stationary box requiring a push to start moving and a moving box needing a force to come to a stop.
- Newton's third law emphasizes that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction, showcasing the interconnectedness of forces and interactions in the physical world.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is Newton's first law?
An object stays at rest or in motion unless acted upon.
What does Newton's second law state?
Force equals mass times acceleration.
What is Newton's third law?
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
What are some types of forces?
Weight, normal force, friction, tension, air resistance.
What is a free body diagram?
A diagram showing forces acting on objects.
Related videos
The Organic Chemistry Tutor
Newton's Law of Motion - First, Second & Third - Physics

LearnFree
Newton's Laws of Motion (Motion, Force, Acceleration)

Physics Wallah - Alakh Pandey
Class 11 Chap 5 || Laws Of Motion 01 || Newton's First Law Of Motion || NLM IIT JEE NEET NCERT

LearnoHub - Class 11, 12
Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 One Shot | New NCERT CBSE

Webster Science
Chapter 4 Newton's 2nd Law of Motion Lecture 1 Force Causes Acceleration / Friction / Mass & Weight
Summary
00:00
Newton's Laws: Forces and Motion Explained
- Newton's first law states that an object remains at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force.
- Two cases illustrate this law: a 10kg box at rest requires external force to move, while a moving box needs force to stop.
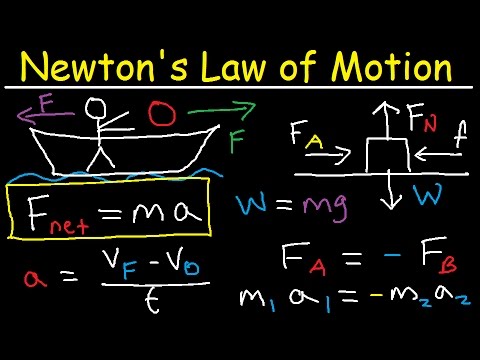
- Newton's second law equates net external force to mass times acceleration, expressed as F=ma in newtons.
- The SI unit for force is kilogram meter per second square or newton (N).
- Newton's third law states that every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
- Various types of forces include weight, normal force, friction, tension, and air resistance.
- Weight is the gravitational pull on an object, normal force is perpendicular to contact surfaces, and friction opposes motion.
- Tension is a pulling force exerted by a string, while air resistance opposes an object's motion through air.
- Aerodynamic lift is created by air pressure differences above and below a moving vehicle.
- Free body diagrams show forces acting on objects, aiding in problem-solving involving forces.




