Das Gehirn: Aufbau und Funktion einfach erklärt - Cortex
David Rau・9 minutes read
The brain, consisting of the cerebellum, brainstem, and cerebrum, controls vital functions like movement coordination and human intelligence through its cortex divided into four lobes with specific functions.
Insights
- The brain is divided into distinct regions with specialized functions, such as the cerebellum coordinating movement and the cortex in the cerebrum responsible for human intelligence.
- The cortex, divided into four lobes, each serves specific roles, highlighting the brain's complexity and the intricate coordination required for various functions like decision-making and visual perception.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What are the main parts of the brain?
The brain consists of the cerebellum, brainstem, and cerebrum, each with distinct functions.
What does the cerebellum control?
The cerebellum coordinates movement and is densely packed with neurons.
How is human intelligence linked to the brain?
Human intelligence is attributed to the cortex in the cerebrum due to its convolutions.
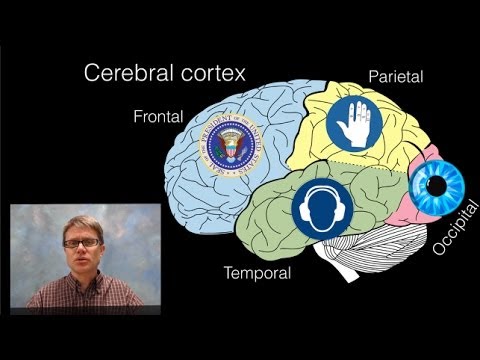
What are the four lobes of the cortex?
The cortex is divided into frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes, each with specific functions.
What functions are associated with the frontal lobe?
Decision-making is a key function of the frontal lobe, contributing to cognitive processes and behavior.
Related videos

EZmed
Lobes of the Brain: Cerebrum Anatomy and Function [Cerebral Cortex]
Bozeman Science
The Brain

AnatomyZone
Basic Parts of the Brain - Part 1 - 3D Anatomy Tutorial

Khan Academy India - English
Brain: Parts & functions (Fore, mid & hind) | Control & Coordination | Biology | Khan Academy

RajNEET Medical Education
Parts of brain in Hindi | Fore Brain | Mid Brain | Hind Brain | Cerebellum | Functions | Location
Summary
00:00
Understanding the Complex Functions of the Brain
- The brain is complex and not fully understood, but some key functions are known.
- The brain consists of the cerebellum, brainstem, and cerebrum, with common areas shared with all mammals.
- The cerebellum coordinates movement and is densely packed.
- The brainstem and diencephalon control vital functions like swallowing and hormone regulation.
- The cortex in the cerebrum is responsible for human intelligence due to its convolutions.
- The cortex is divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal.
- Each lobe has specific functions, such as decision-making in the frontal lobe and visual perception in the occipital lobe.




