Class 11 Biology cell biology part 3
Department Of Information Technology・2 minutes read
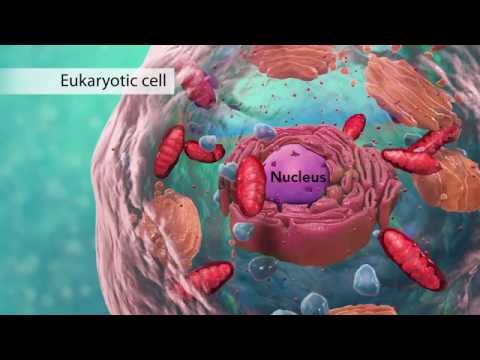
The nucleus, essential to eukaryotic cells, is a dark, dense, spherical structure absent in prokaryotic cells, with exceptions in certain organisms like mature red blood cells and mammalian cells. Mitosis, a key phase in the cell cycle, involves the division of the nucleus into two daughter cells, aiding in growth, development, and reproduction, as well as maintaining a constant number of chromosomes in body cells.
Insights
- The nucleus is a defining feature of eukaryotic cells, distinguished by its dark, dense, spherical structure and the presence of a nuclear membrane, absent in prokaryotic cells.
- Chromosomes, containing DNA and genes, play a crucial role in heredity and cell division, with variations in centromere position leading to different types of chromosomes, impacting appearance during anaphase and ensuring equal genetic distribution in daughter cells during mitosis.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the nucleus?
The nucleus is a dark, dense, spherical structure in eukaryotic cells.
What is the study of the nucleus called?
The study of the nucleus is known as cardiology.
What are chromosomes made of?
Chromosomes are formed from condensed chromatin fibers.
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a phase in the cell cycle where the nucleus divides into two daughter cells.
Why is mitosis important?
Mitosis is crucial for growth, development, and maintaining genetic stability.
Related videos

Ninja Nerd
Cell Nucleus Structure & Function

Professor Dave Explains
Eukaryotic Cells Part 1: Animal Cells and Endosymbiotic Theory

Dr. Julie Wells
Chapter 4: Eukaryotic Cells
Nucleus Medical Media
Biology: Cell Structure I Nucleus Medical Media

Biologie - simpleclub
Was sind eukaryotische und prokaryotische Zellen?!
Summary
00:00
Nucleus: Key Component of Eukaryotic Cells
- The nucleus is a key component of a eukaryotic cell, characterized by its dark, dense, spherical structure.
- It is absent in prokaryotic cells but distinct in eukaryotic cells due to the presence of a nuclear membrane.
- The incipient nucleus, found in prokaryotic cells, lacks a nuclear membrane, while the dark, dense, spherical nucleus is typical of eukaryotic cells.
- Exceptions to the presence of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells include certain organisms like mature red blood cells and mammalian cells.
- The study of the nucleus is known as cardiology, and it was first discovered by Robert Brown in 1831.
- Eukaryotic cells may contain one or more nuclei, with examples like muscle cells having multiple nuclei.
- Multinucleate cells, like those in Paramecium, can have more than two nuclei, showcasing variability in the number of nuclei per cell.
- Chromosomes are formed from condensed chromatin fibers, transitioning from a diffuse structure to a more defined, shorter, and thicker form.
- The structure of a chromosome includes a centromere, primary constriction, kinetochores, and secondary constrictions.
- Chromosomes also contain nucleolus, chromonema, and chromatids, with each chromatid forming a single chromosome when joined at the centromere.
19:53
Chromosomes and Cell Division: An Overview
- Chromosomes can be classified based on the position of the center, determining the type of chromosome.
- Chromosomes can be categorized as metacentric, submetacentric, acrocentric, or telocentric based on the position of the centromere.
- The position of the centromere affects the appearance of chromosomes during anaphase, leading to different sets of chromosomes.
- The nucleus contains the chromosome, which carries hereditary material and helps transfer information between generations.
- DNA is the hereditary material contained in chromosomes, with each chromosome containing multiple genes.
- Cell division is essential for growth, development, and reproduction, with two main objectives being growth and reproduction.
- Cell division can be direct or indirect, with direct cell division involving no spindle fibers or chromosome separation.
- Mitosis is a phase in the cell cycle where the nucleus divides into two daughter cells, consisting of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Karyokinesis is the phase in the cell cycle where the nucleus divides, involving prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- During prophase, the nuclear membrane and nucleolus remain intact, while the chromatid fibers condense.
40:32
"Mitosis: Chromosome Condensation and Cell Division"
- Chromatin fibers condense to form cell chromosomes during prophase, with each chromosome containing two chromatids joined at the centromere.
- Mitosis is crucial for growth and development in multicellular organisms, aiding in repairing damaged cells and replacing old or unused ones.
- Mitosis helps in maintaining a constant number of chromosomes in body cells, ensuring stability and equal distribution of genetic material.
- Asexual reproduction, especially vegetative propagation, is facilitated by mitosis, allowing for the duplication of plants without the need for seeds or sexual reproduction.




