Ch 06 Lecture Presentation Video
Reggie Cobb・2 minutes read
Metabolism includes the chemical reactions in cells that transform energy, with photosynthesis and cellular respiration being interconnected processes crucial for energy transfer, where plants convert solar energy into chemical energy and consumers break it down. Enzymes facilitate these metabolic reactions by lowering activation energy, with their activity influenced by factors such as temperature and pH, emphasizing the dynamic nature of energy flow and the importance of understanding these processes in biological systems.
Insights
- Metabolism is a comprehensive process involving all chemical reactions in cells, categorized into building up (anabolic) and breaking down (catabolic) reactions, with energy flow being a central theme; it highlights the roles of producers, like plants, in converting solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis, which is then utilized by consumers, such as animals, during cellular respiration to release energy.
- Enzymes are crucial facilitators of metabolic reactions, acting as catalysts that lower the activation energy needed for reactions to occur; they exhibit specificity for substrates and their activity can be influenced by factors such as temperature and pH, demonstrating the importance of optimal conditions for efficient metabolic processes.
- The interconnectedness of photosynthesis and cellular respiration forms a vital redox cycle in nature, where the products of one process serve as the reactants for the other, emphasizing the flow of energy from the sun through these processes, ultimately culminating in ATP generation, which powers various cellular functions and highlights the dynamic nature of energy transfer in living organisms.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is metabolism in simple terms?
Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions in cells.
How do enzymes function in reactions?
Enzymes lower activation energy for reactions.
What is the role of ATP in cells?
ATP is the main energy carrier in cells.
What are exergonic and endergonic reactions?
Exergonic reactions release energy; endergonic require energy.
How does photosynthesis relate to cellular respiration?
Photosynthesis produces glucose for cellular respiration use.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
Understanding Metabolism and Energy Flow
- Metabolism encompasses all chemical reactions in cells, including both the building up (anabolic) and breaking down (catabolic) of substances, and is divided into four sections: energy flow in cells, metabolic reactions and energy transformations, metabolic pathways and enzymes, and oxidation-reduction reactions in metabolism.
- Energy is defined as the ability to do work or cause change, with two main types: kinetic energy (energy of motion) and potential energy (stored energy that can become kinetic), exemplified by mechanical energy and chemical energy from food, respectively.
- The ultimate source of energy for all organisms is the sun, which provides solar energy that plants convert into chemical energy through photosynthesis, producing carbohydrates that serve as energy sources for consumers.
- The laws of thermodynamics are crucial to understanding energy transfer: the law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed, while the law of entropy indicates that energy transformations are not 100% efficient, with some energy lost as heat.
- Producers, such as plants, build up chemical energy through photosynthesis, while consumers, including animals, break down these chemicals to release energy, utilizing mitochondria for cellular respiration to convert carbohydrates into usable energy.
- Metabolism is the sum of all cellular chemical reactions, with reactants on the left side of a reaction equation and products on the right, and free energy refers to the energy available to perform work in these reactions.
- Enzymes play a critical role in facilitating metabolic reactions by lowering the activation energy required for reactants to convert into products, thus enabling the flow of free energy.
- Exergonic reactions release energy, typically in the form of ATP, during the breakdown of larger molecules into smaller ones, while endergonic reactions require energy input to build larger molecules from smaller ones, such as in photosynthesis.
- ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the primary energy carrier in cells, generated from ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and inorganic phosphate during exergonic reactions, and is essential for driving endergonic reactions in metabolism.
- The ATP cycle involves the continuous conversion between ATP and ADP, where energy released from exergonic reactions is captured in ATP, which then provides energy for various cellular processes, highlighting the dynamic nature of energy flow in biological systems.
17:32
ATP ADP Cycle and Enzyme Function Explained
- Exergonic reactions involve hydrolysis, where ATP is broken down to release a phosphate group, converting ATP to ADP, which is essential for processes like protein synthesis, nerve conduction, and muscle contraction.
- The cycle of ATP and ADP is crucial; ATP releases energy through the breakdown process, and ADP can then capture a phosphate group during cellular respiration to regenerate ATP, illustrating the continuous cycle of energy transfer.
- Muscle contraction is initiated by ATP, which binds to myosin, causing a shape change that allows myosin to pull on actin, resulting in muscle contraction. The release of ADP and phosphate further facilitates this process.
- Metabolic pathways consist of a series of reactions where the product of one reaction serves as the substrate for the next, demonstrating a step-by-step progression from initial reactants to final products.
- Enzymes, which are proteins that act as catalysts, are specific to certain reactions and substrates, helping to accelerate reactions without being consumed in the process.
- The activation energy is the minimum energy required to initiate a reaction, and enzymes lower this energy requirement, allowing reactions to proceed more efficiently.
- The enzyme-substrate complex forms when an enzyme binds to its specific substrate at the active site, leading to a change in shape that facilitates the reaction, known as the induced fit model.
- Degradation reactions involve enzymes breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones, while synthesis reactions involve enzymes combining substrates to form larger molecules, both essential for metabolism.
- Factors affecting enzymatic activity include substrate concentration, optimal pH, and temperature; higher substrate concentrations increase enzyme activity due to more frequent collisions, while each enzyme has a specific pH and temperature range for optimal function.
- Enzymatic activity generally increases with temperature, as warmer conditions enhance molecular collisions, but extreme temperatures can denature enzymes, reducing their effectiveness.
34:50
Enzyme Activity and Its Environmental Influences
- Enzymes function optimally at specific temperatures, typically around 40 degrees Celsius, but can be denatured at excessively high temperatures unless they are heat-resistant enzymes from extreme environments.
- The effectiveness of enzymes is also influenced by pH levels; for example, pepsin operates best at a pH of 2, while trypsin is most effective at a pH of 8, indicating that different enzymes have specific pH ranges for optimal activity.
- Ectothermic animals rely on external heat sources to regulate their body temperature and enzyme activity, while endothermic animals maintain a stable internal temperature that supports enzymatic reactions, crucial for cellular function.
- The coloration of Siamese cats is affected by temperature, demonstrating that enzyme activity can influence physical traits, as their coloration varies based on whether they live indoors or outdoors.
- Enzyme activity is regulated by cofactors and coenzymes; cofactors are inorganic molecules that assist enzyme function, while coenzymes are organic molecules, often derived from vitamins, that are necessary for enzyme activity.
- Enzyme inhibition can occur through competitive inhibition, where an inhibitor competes with the substrate for the active site, or non-competitive inhibition, where the inhibitor binds to an allosteric site, altering the enzyme's shape and preventing substrate binding.
- In metabolic pathways, the accumulation of end products can lead to non-competitive inhibition, where the end product binds to the allosteric site, signaling the enzyme to stop further production when sufficient product is formed.
- Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, involve the transfer of electrons; oxidation refers to the loss of electrons, while reduction refers to the gain of electrons, often remembered by the acronyms "LEO" (Lose Electrons = Oxidation) and "GER" (Gain Electrons = Reduction).
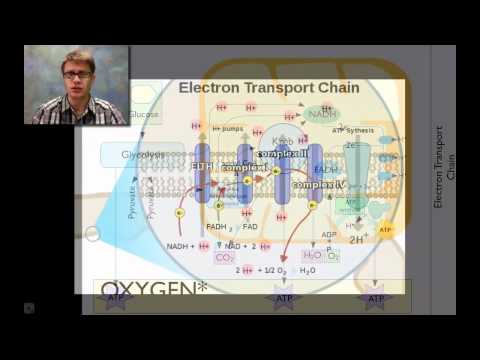
- Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, where solar energy converts water and carbon dioxide into glucose, storing approximately 686 kilocalories of energy, while cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria, breaking down glucose to produce ATP and releasing carbon dioxide and water.
- Both photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected; the products of one process serve as the substrates for the other, with carbon dioxide being reduced in photosynthesis and carbohydrates being oxidized in cellular respiration, forming a redox cycle essential for energy transfer in living organisms.
54:18
Energy Flow in Cellular Respiration Explained
- In cellular respiration, carbon carbohydrates are oxidized, and energy flows from the sun through photosynthesis to cellular respiration, ultimately becoming unstable heat when ATP is utilized by the cell; this process is not a cycle but a linear flow of energy, emphasizing the importance of understanding energy dynamics and enzyme functions in cells for comprehending subsequent chapters on photosynthesis and cellular respiration, which detail the buildup and breakdown of ATP and the role of energy-carrying molecules in transporting and releasing hydrogens.