BTEC Applied Science: White Blood Cells
BTEC Applied Science Help・9 minutes read
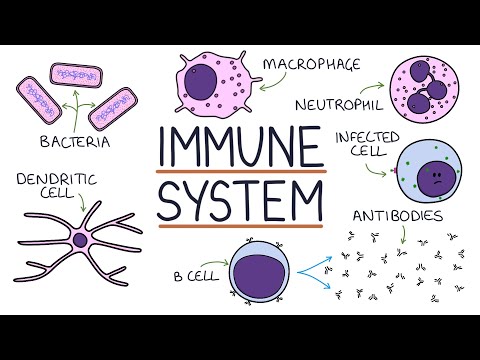
White blood cells are vital for the immune system, with neutrophils being nonspecific and lymphocytes targeting specific pathogens. Recognizing these differences is crucial for understanding their roles in immunity.
Insights
- White blood cells play a vital role in the immune system by combating pathogens like bacteria and viruses that enter the body, with neutrophils being nonspecific in engulfing and digesting pathogens, while lymphocytes, such as B and T cells, are specific in targeting pathogens.
- The distinction between neutrophils and lymphocytes is crucial; neutrophils are more prevalent and nonspecific, while lymphocytes are specific and recognize particular pathogens, emphasizing the importance of understanding these differences for a comprehensive grasp of the immune system's functions.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the role of white blood cells?
White blood cells are essential for the body's immune system, fighting off pathogens like bacteria and viruses that enter the body. They travel through blood vessels and capillary pores to reach tissues, using their flexibility and lobed nucleus structure to navigate effectively.
What is the function of neutrophils?
Neutrophils, the most common type of white blood cells, are nonspecific in their approach to combating pathogens. They engulf and digest pathogens using enzymes in their lysosomes, playing a crucial role in the body's defense against infections.
How do lymphocytes differ from neutrophils?
Lymphocytes, including B and T cells, are specific in targeting pathogens compared to neutrophils. They have receptors that aid in recognizing particular pathogens, allowing them to mount a targeted immune response against specific threats.
Why is it important to understand white blood cell types?
Understanding the differences in white blood cell types and their functions is crucial for comprehending their roles in the immune system. Neutrophils are more prevalent and nonspecific, while lymphocytes are specific and recognize particular pathogens, highlighting the diverse strategies employed by the immune system to protect the body.
How do white blood cells combat pathogens?
White blood cells combat pathogens like bacteria and viruses by traveling through blood vessels and capillary pores to reach tissues. Neutrophils engulf and digest pathogens nonspecifically, while lymphocytes, such as B and T cells, target specific pathogens using receptors for recognition. This coordinated effort by different types of white blood cells is vital for the body's immune response against infections.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
White Blood Cells: Immune System Defenders
- White blood cells are crucial for the body's immune system, combating pathogens like bacteria and viruses that enter the body.
- They travel through blood vessels and pass through capillary pores to reach tissues, aided by their flexibility and lobed nucleus structure.
- Neutrophils, the most common white blood cells, are nonspecific, engulfing and digesting pathogens with enzymes in their lomes.
- Lymphocytes, including B and T cells, are specific in targeting pathogens, with receptors aiding in pathogen recognition.
- Neutrophils are more prevalent and nonspecific, while lymphocytes are specific and recognize particular pathogens.
- Understanding the differences in white blood cell types and their functions is essential for grasping their roles in the immune system.