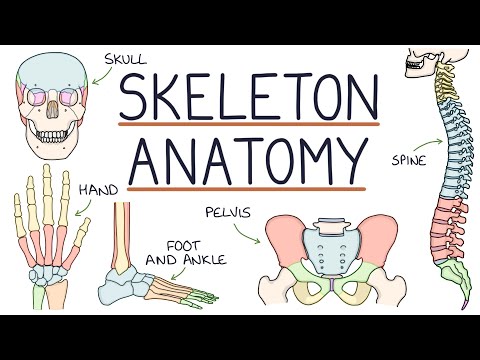
Bone Anatomy and Physiology in Hindi | Bone cells | compositions | Types | Structure | Functions
RajNEET Medical Education・12 minutes read
The human body's framework is primarily composed of bones, providing structure and support while playing a crucial role in growth and renewal. Bone growth involves continuous remodeling and repair, with joints essential for mobility and the production of blood cells in bone marrow.
Insights
- Bones are pivotal for the human body's framework, supporting mobility and providing structure through a complex system involving mineral balance, blood vessels, tendons, and ligaments.
- The growth and maintenance of bones are intricate processes influenced by factors like diet, joint health, and the continuous remodeling by osteoclasts and osteoblasts, with cartilage and spongy bones playing crucial roles in bone development and health.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the function of bones in the human body?
Bones provide structure, support, and aid in mobility.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
"Essential role of bones in human body"
- The human body's framework is primarily composed of bones, providing structure and support.
- Adults typically have 206 bones in their skeleton, while infants or newborns may have around 300 bones.
- Bones play a crucial role in our body's structure, growth, and constant renewal.
- Connective tissue formation in the body is influenced by diet, particularly the intake of collagen-producing proteins.
- Joints, like the Pradhya Joint, are essential for mobility and function, with red blood cells, white blood cells, and blood platelets being produced in the bone marrow.
- The bone growth process involves the continuous remodeling and repair of bone tissue by osteoclasts and osteoblasts.
- Cartilage is crucial for bone growth, with the growth plates closing around the age of 18 to 21 years.
- The structure and shape of bones are maintained by a balance of minerals, blood vessels, tendons, and ligaments.
- The bone structure includes compact and spongy bones, with the latter resembling a sponge under a microscope and playing a vital role in maintaining bone health.