6 Pulley Problems
Physics Ninja・2 minutes read
The Physics Ninja presents six pulley problems focusing on calculating acceleration and tension by assuming the pulley's mass is negligible and ignoring rope weight. Problems involve free body diagrams, application of Newton's laws, and calculating acceleration and tension values, such as 0.89 m/s^2 and 8.9 N in Problem 1. In more complex scenarios, like a pulley system with six pulleys suspending a 300-kilogram mass, analysis of forces and application of Newton's laws reveal the force needed to lift (490 N) and accelerate (740 N) the mass.
Insights
- The key to solving pulley problems in physics is assuming the pulley's mass is negligible and ignoring the rope's weight. The focus is on calculating acceleration and tension, often requiring the application of Newton's laws and the breakdown of forces into components for accurate solutions.
- Analyzing forces acting on blocks, applying Newton's laws, and considering additional factors like slopes or multiple ropes are crucial in solving complex pulley problems. By establishing coordinate systems, breaking down forces, and carefully calculating acceleration and tension, accurate solutions can be obtained, showcasing the intricacies involved in these physics scenarios.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
How can I solve pulley problems in physics?
By assuming negligible pulley mass, ignoring rope weight, and calculating acceleration and tension using Newton's laws.
What is the key to solving pulley problems?
Assuming pulley mass is negligible and ignoring rope weight.
What forces are essential in pulley problem analysis?
Weight, normal force, and tension acting on the blocks.
How do you calculate acceleration in pulley problems?
By applying Newton's second law to determine acceleration.
What is the recommended approach for analyzing pulley systems?
Place objects in a box, analyze forces acting on the box, consider tension in ropes, and weight of objects.
Related videos

Arjuna JEE
Friction FULL CHAPTER | Class 11th Physics | Arjuna JEE
Michel van Biezen
Physics - Mechanics: The Pulley (1 of 2)
Michel van Biezen
Mechanical Engineering: Particle Equilibrium (11 of 19) Why are Pulleys a Mechanical Advantage?

Michel van Biezen
Physics 17 Tension and Weight (1 of 11) What is Tension?

JEE Wallah
NEWTON LAW OF MOTION in 110 Minutes || Full Chapter Revision || Class 11th JEE
Summary
00:00
Solving Pulley Problems in Physics
- Physics Ninja presents six pulley problems commonly seen in AP Physics and undergraduate physics.
- The key to solving these pulley problems is to assume the pulley's mass is negligible compared to the blocks and to ignore the weight of the rope.
- The focus is on calculating acceleration and tension in all problems.
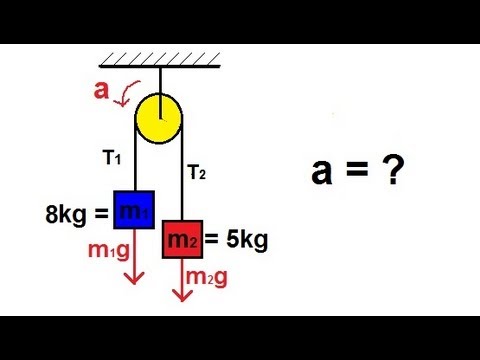
- Problem 1 involves two blocks, Big M and little m, connected without friction. The goal is to find the system's acceleration.
- A free body diagram is essential, showing forces like weight, normal force, and tension acting on the blocks.
- Newton's second law is applied to both blocks to determine acceleration and tension.
- By adding the equations for both blocks, the acceleration can be calculated by dividing the total mass of the system.
- The acceleration is approximately 0.89 m/s^2, and the tension is 8.9 Newtons.
- Problem 2 features two hanging masses connected by a rope over a pulley. The same method is used to find acceleration and tension.
- The acceleration is around 8 m/s^2, and the tension is 17.8 Newtons.
- Problem 3 introduces a block on a slope, requiring consideration of additional forces like the normal force. The same approach is used to determine acceleration and tension.
13:59
Forces and Acceleration in Block Systems
- Coordinate system established for block on slope
- Forces broken down into X and Y components
- Normal force and tension force directions clarified
- Weight broken down into perpendicular and parallel components
- Newton's first and second laws applied to big and small blocks
- Normal force calculated as mg cos theta
- Acceleration calculated for big block and small block
- Tension force determined as 13.4 Newtons
- Similar problem with small block on slope introduced
- Forces analyzed for big and small blocks on slope
- Acceleration calculated as 0.62 m/s^2
- Tension force calculated as 6.2 Newtons
- Pulley system with single string and two blocks explained
- Forces analyzed for block M in pulley system
- Force F required for constant speed of 2 m/s calculated as 14.7 N
- Force F required for upward acceleration of 5 m/s^2 calculated as 22.2 N
29:09
Analyzing Forces in Pulley Systems
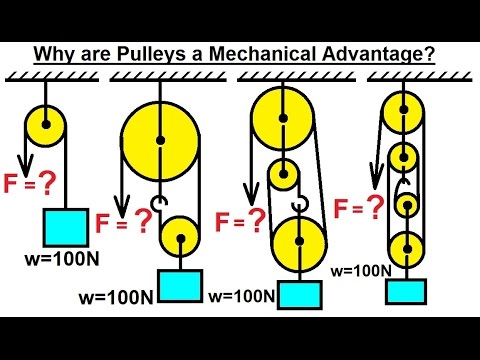
- When dealing with a pulley system with multiple ropes, it is advised to place the objects in a box and analyze the forces acting on the box, considering the tension in the ropes and the weight of the objects.
- In a scenario where a 300-kilogram mass is suspended from a pulley system with six pulleys, pulling down with a force F creates a tension throughout the rope. By applying Newton's second law and considering the forces acting on the box, the force required to lift the mass is calculated to be 490 Newtons, which is advantageous due to the mechanical advantage of the pulley system.
- To accelerate the mass upward, the force required increases to 740 Newtons, as the net force acting on the system is unbalanced, necessitating a greater force to achieve the desired acceleration.




